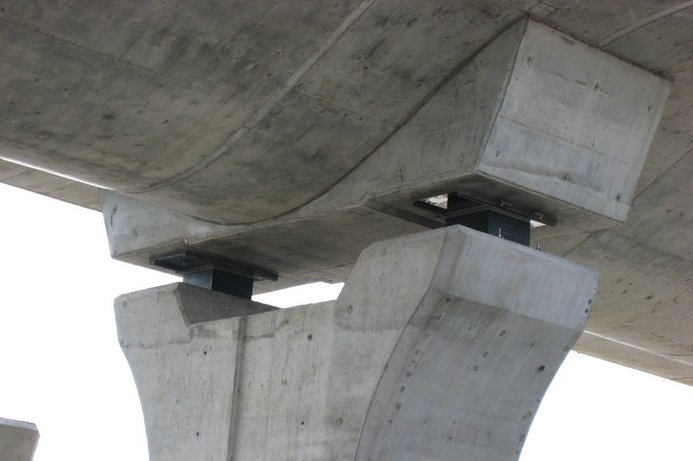
ELASTOMERIC BEARINGS
A wide range of loads can be accommodated by varying the plan area, the thickness of internal elastomer layers and the elastomer hardness. Plan areas should be chosen on the basis of bearing seat dimensional limitations as well as loads. Changing the elastomer hardness and increasing the effective thickness by adding layers are methods of varying the resistance to horizontal movement and the amount of such movement. Beam end rotations up to about 0.02 radians can readily be accepted by adding to the effective elastomer thickness. Bearings can be molded in rectangular shape. Plain Elastomeric Pads, without internal shim plates, can also be supplied by River. These Plain Elastomeric Pads can be molded the same as Laminated Bearing Pads.


Why use elastomeric bearings?
There is good reason for this. They support vertical loads with minimal compression, allow expansion and contraction of the structure with minimal resistance and provide for normal end rotation of bridge beams. In addition, they are easily installed and maintenance -free. All this is encompassed in a unit having the lowest cost per unit of supported load up to approx. 1500 kN. More sophisticated designs can be incorporated into an integrated structural system that channels horizontal loads to strong points and away from weaker ones. Ultimately such systems are used to mitigate the severe loading conditions caused by earthquakes. River Team is pleased to offer Laminated Steel/Elastomer Bearings to suit any owner or State Specifications. With our extensive design experience, we can readily provide designs for specialty applications to meet unique design criteria or specific design requirements.
STRUCTURAL DESIGN — ELASTOMERIC BEARINGS
are normally mounted with their short side parallel to the girder axis for maximum rotation capacity. However, orientation at any angle in the horizontal plane will not affect the shear resistance. Friction is usually sufficient to keep bearings in place, but if minimum loads are light, then a slippage check must be made; use a friction coefficient of 0.2 between elastomer and steel or pre-cast concrete. A coefficient of 0.3 may be used for elastomer against broom-finished concrete or similar roughened surface. If positive location is required, vulcanized bonding to steel plates is suggested.

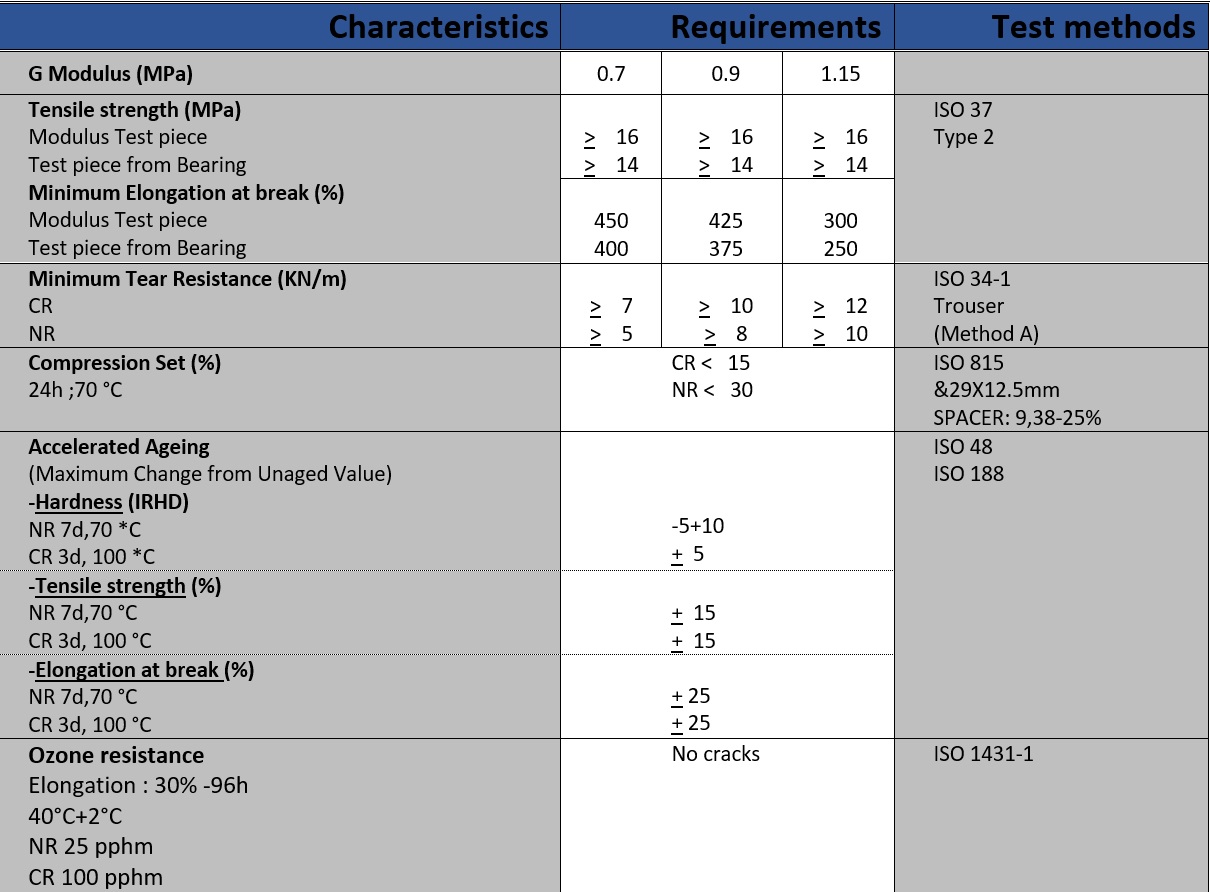
Elastomer material charectristics
The elastomer used in the machining process can be polychloroprene (CR), natural rubber (NR) according to the required specifications.
The elastomer Hardness shore 60±5 with shear modulus 0.9±0.15 N/mm2 in accordance with the European Standard Code EN 1337-3.
The mechanical properties of the elastomer are shown in the table below.
Quality Control
Rubber
is compounded in internal mixers, Quality is monitored round the clock by continuously testing samples for their physical properties and chemical characteristics. Every ingredient is checked and monitored regularly, in-process inspection is also conducted at various stages of production, during performance testing and while the final inspection is carried out. Our products are certified to meet the most demanding requirements of civil construction, oil and gas, infrastructure, marine and military applications.

Quality
is a key point of River manufacturing system as we are keen on Preforming tests Periodically on our Raw Materials and Final products according to EN-1337-3 From Accredited Testing Labs.

A Quality Control Department
at highly qualified engineers equipped with the most modern testing equipment to ensure quality of every stage of production, the function of the quality control starts from the inspection of incoming raw material and continues through the various stages of production, until the final finished product moves out of the company.
Our department is highly dedicated to ensuring the product quality satisfies customer requirements.

Product Types
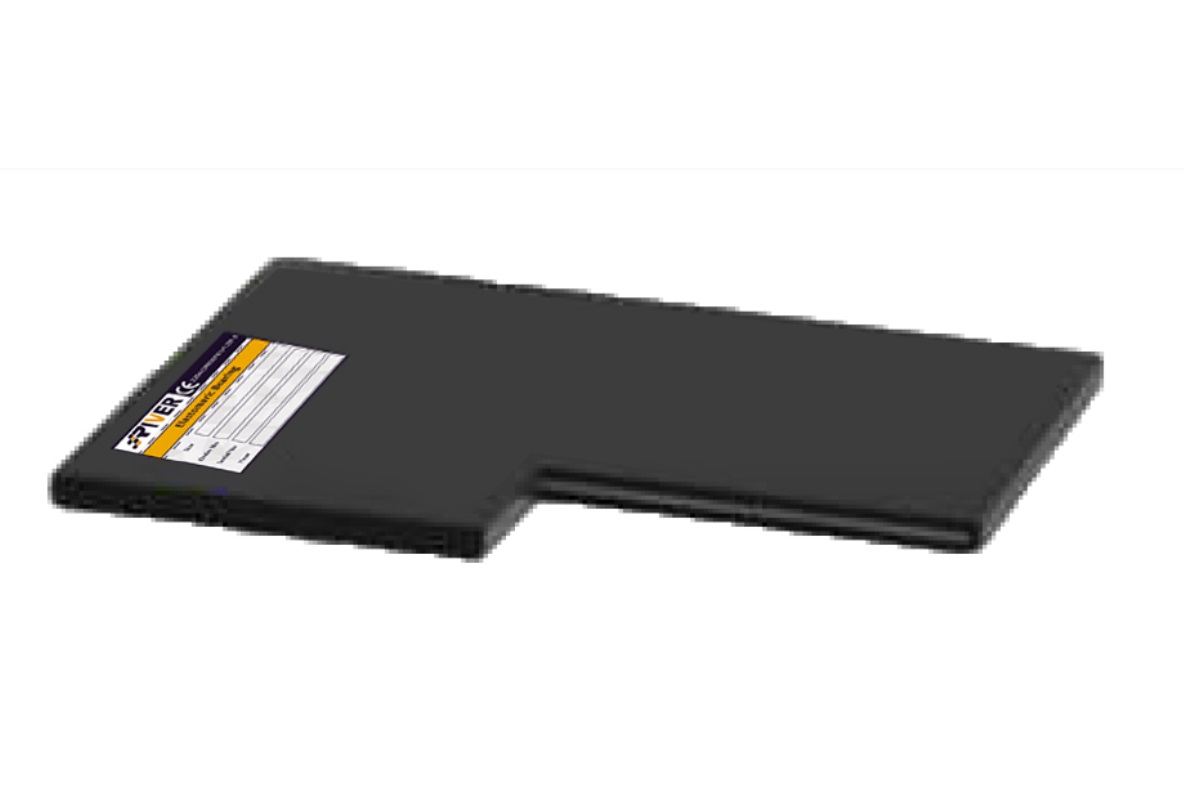

Elastomeric A
This bearing, fully covered with elastomer, comprising only one steel reinforcing plate
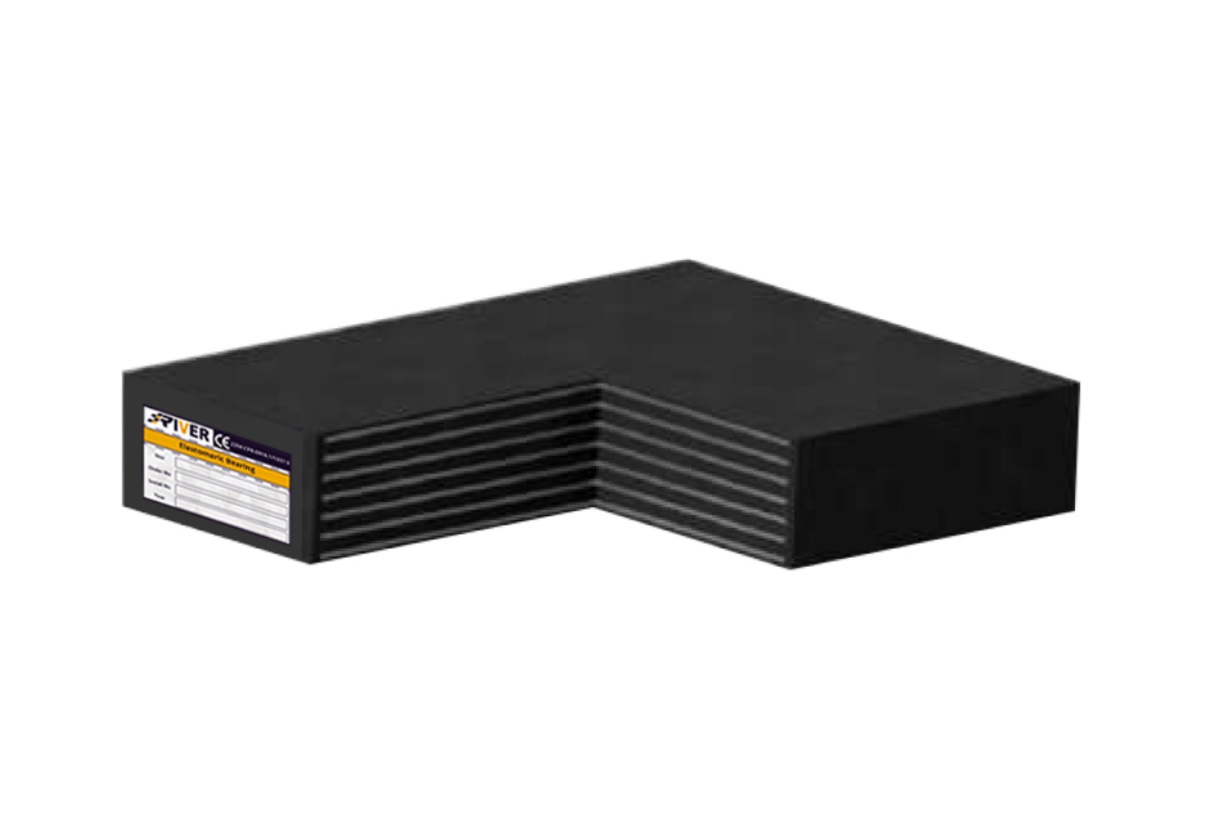

Elastomeric B
This bearing fully covered with elastomer, comprising at Least two steel reinforcing plates;
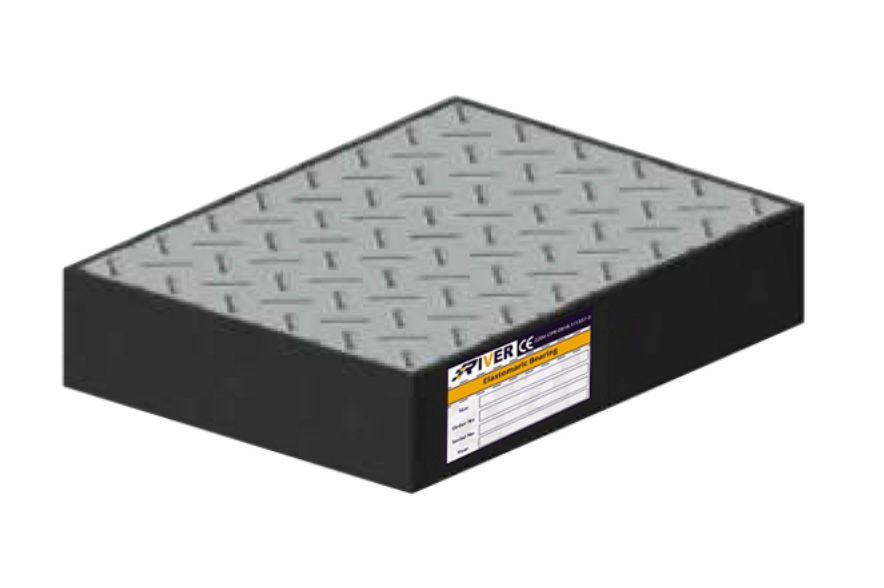

Elastomeric C4
This type of bearing also features external Checker plates, vulcanized into its upper and lower surfaces On the surface enabling installation directly
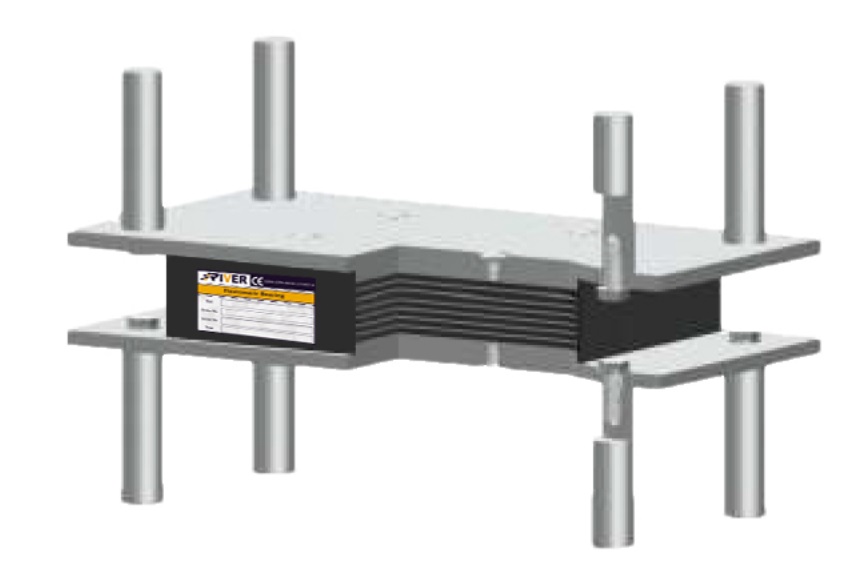

Elastomeric C2
This type of bearing also features external Steel plates, vulcanized into its upper and lower surfaces; allows external connections to steel plates with shear Dowels or bolts. The bearing can be replaced simply by minimum lifting the structure, since there are no embedded anchoring elements.
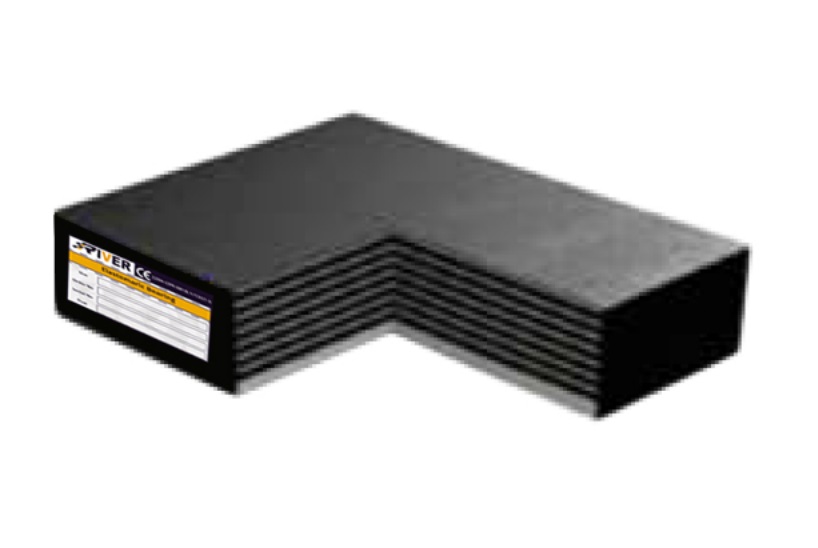

Elastomeric B/C
These types of bearing are Combination of Types B and C, with only one side featuring an external Steel Plate.
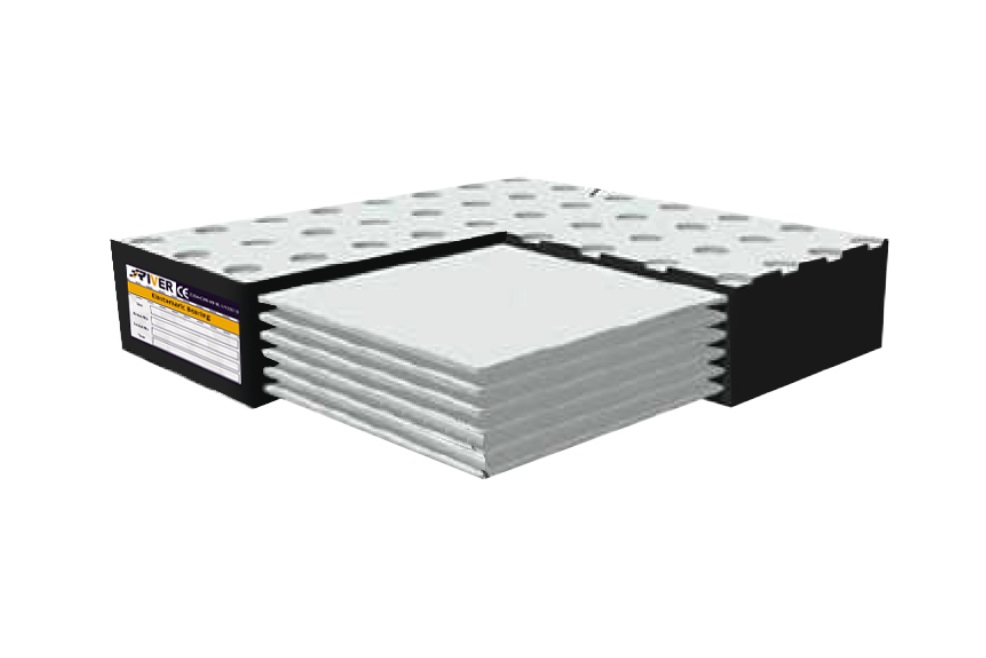

Elastomeric D
This type of bearing is same as Type B but with PTFE plate vulcanized in to its upper surface.
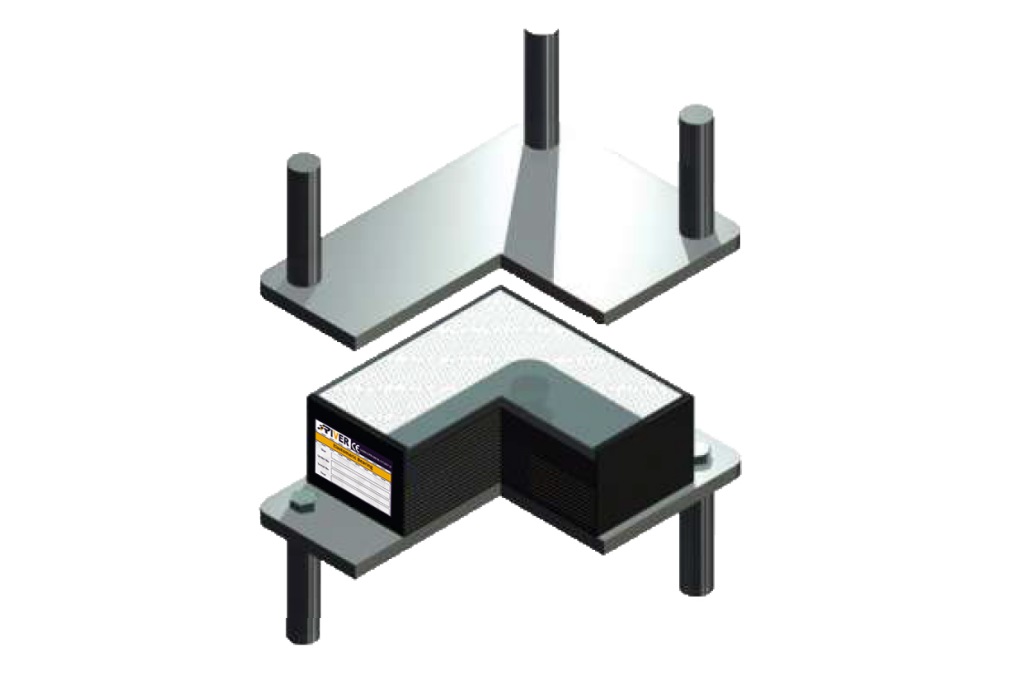

Elastomeric E
This type of bearing is same as Type C with PTFE plate vulcanized in to its outer steel plate.
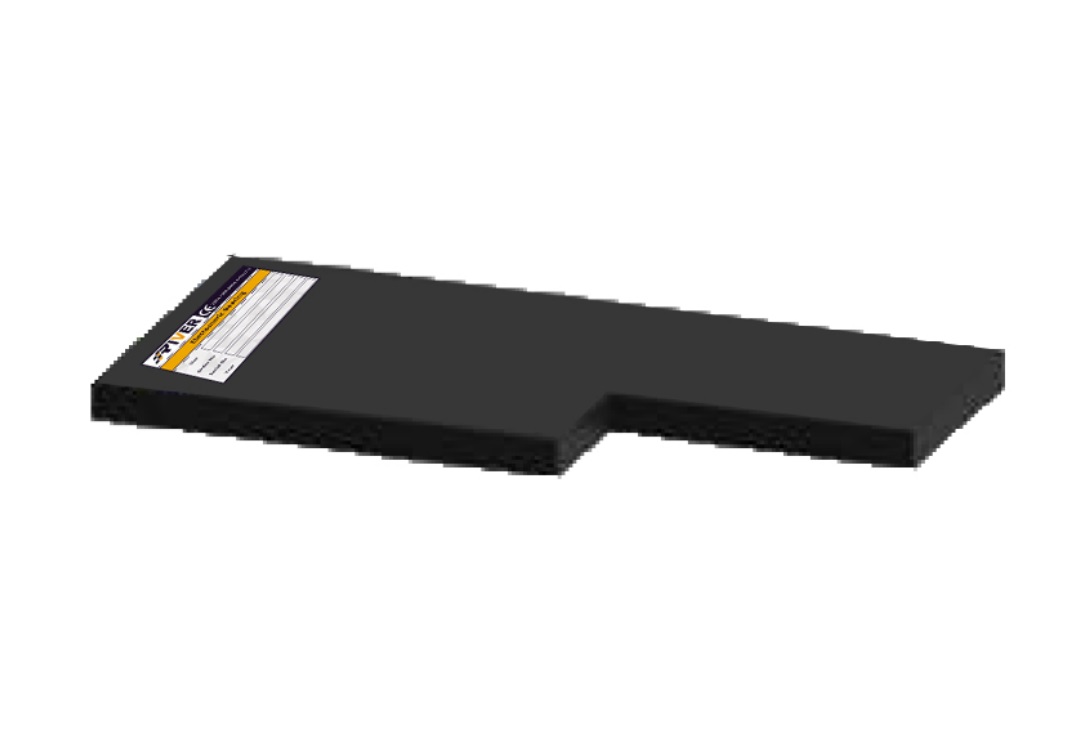

Elastomeric F
This type of bearing made only of rubber (not reinforced). They are used when vertical load and horizontal displacement are small.
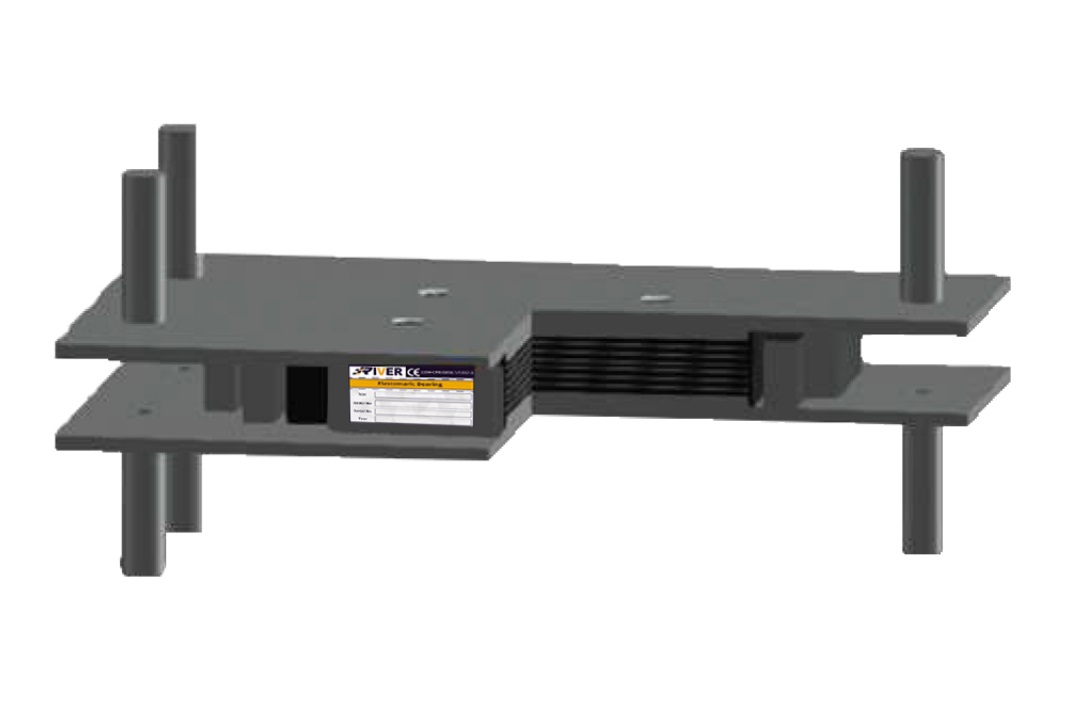

Elastomeric Fixed bearing
Same as Type C between 2 steel plates with welded restraints to transfer the horizontal Loads in every direction. They prevent horizontal displacements in any direction.
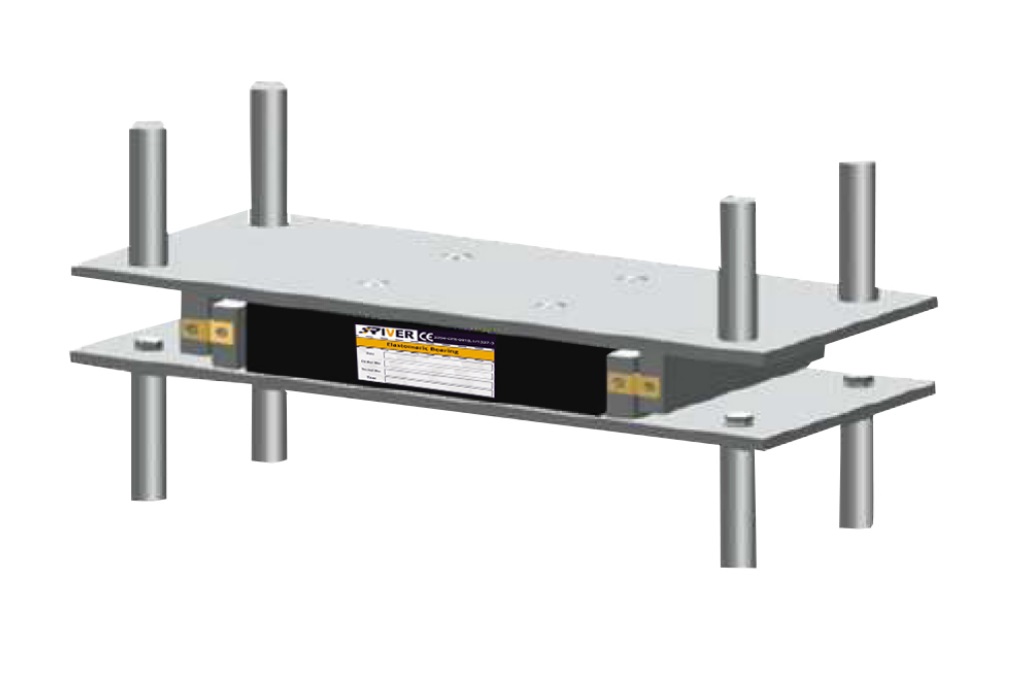

Elastomeric Guided bearing
Same as Type C between 2 steel plates with welded restraints to transfer the horizontal load in the transversal direction. They allow horizontal displacements only along 1 direction.
